Vitamin A During Pregnancy
dashapetrenkophotos

Written by Mindsmaking Medical Writer
Fact Checked by Mindsmaking Professionals
25th, July, 2025
The intake of Vitamin A during pregnancy is important. So, how much do you need? Here are the recommended intake, risks, and balanced diet for a healthy mother and baby.
Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is essential during pregnancy. Vitamin A during pregnancy helps to improve your baby's vision, keeps your baby's immune system healthy, and supports your baby’s overall development.
However, it is important to take vitamin A in moderation. Not getting enough can lead to issues like night blindness, while too much can be harmful, especially in the early stages of pregnancy.
Getting the right amount of vitamin A helps you and your baby stay healthy during pregnancy.
Do You Need Vitamin A Supplements During Pregnancy?
You're likely getting enough vitamin A if you eat a healthy, balanced diet. The World Health Organization recommends extra vitamin A supplements only if the vitamin is deficient.
This vitamin is important for your eyesight, immune system, and your baby’s growth. However, too much vitamin A, especially from supplements or certain animal foods, can be harmful.
If you live in an area where vitamin A deficiency is common, or have a condition that affects the absorption of nutrients, your healthcare provider may suggest a supplement to help prevent issues like night blindness.
But if you live in a region where foods naturally contain plenty of vitamin A, like in the United States, your body will get enough through diet.
Vitamin A comes from two main sources: natural food sources and synthetic supplements. The two primary natural sources of vitamin A are:
Preformed Vitamin A (Retinol)
These are found in animal products like dairy, eggs, and fish oils. Liver and liver products contain very high levels of vitamin A (retinol), which in large amounts can harm a developing baby. So it’s best to avoid them during pregnancy.
Provitamin A Carotenoids (plant-based)
These vitamins are found in colorful fruits and vegetables like carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, and red peppers. Your body converts them into Vitamin A as needed, making them a good choice and reducing the risk of toxicity. (3)
The synthetic source found in many supplements provides preformed Vitamin A. While these can be effective if you’re deficient, you have to be extra careful because the active form of these synthetic sources can be harmful if taken in excess. So, do not take Vitamin A supplements except if recommended by your healthcare provider.
How Much Vitamin A Is Safe During Pregnancy?
The recommended intake of Vitamin A differs. According to the National Institute of Health(2), expecting moms within the age ranges of 14 to 18 require 750 mcg RAE for 19 to 50 an intake of 770 mcg RAE.
The recommended daily intake for lactating (breastfeeding) moms is 1,200 mcg RAE; for those aged 19 to 50, it is 1,300 mcg RAE.
While vitamin A is very important, having too much, especially the preformed kind, can lead to problems such as birth defects and liver toxicity.
It's advisable to avoid high-dose vitamin A supplements and limit foods rich in retinol, such as liver. Instead, focus on beta-carotene-rich plant sources and your prenatal vitamin.
Benefits Of Vitamin A During Pregnancy
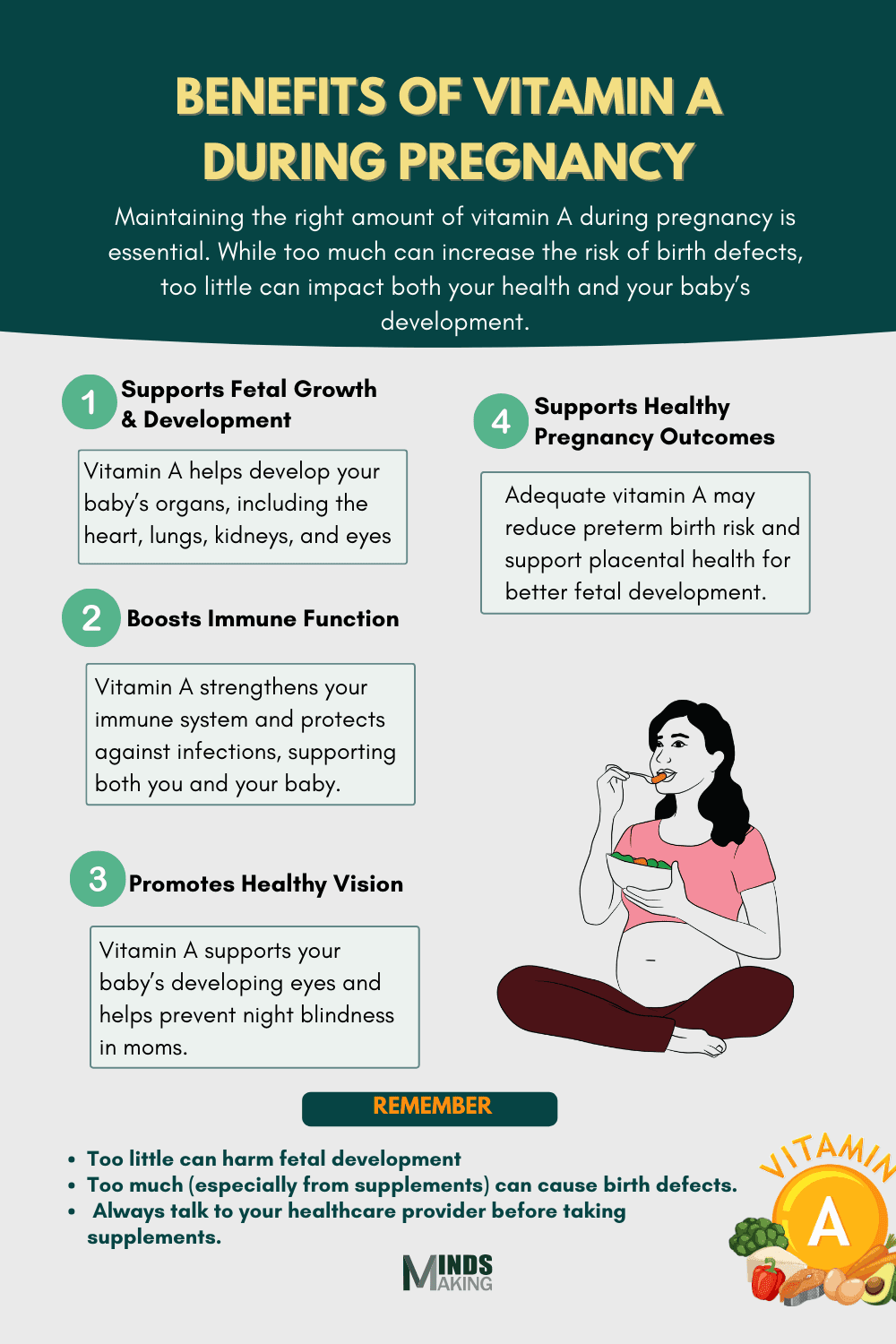
Having the right amount of vitamin A during pregnancy is important. Too much can cause harm to your baby and increase the risk of birth defects, while too little can negatively impact both your health and your baby’s development. (2)
Supports Fetal Growth & Development: Vitamin A is like a building block for your baby’s tiny body. It helps form major organs, including the heart, lungs, and kidneys, and plays a key role in developing their little eyes and vision. Without enough, their growth could be affected, but luckily, a balanced diet with foods like sweet potatoes, carrots, and leafy greens can provide just what your baby needs.
Boosts Immune Function: Pregnancy can make you more susceptible to colds and infections, but vitamin A helps strengthen your body’s defenses. It keeps your skin and mucous membranes (like those in your nose and throat) healthy, acting as a natural barrier against germs. Plus, it gives your baby’s immune system a head start, helping them stay protected even after birth.
Promotes Healthy Vision: Vitamin A is essential for your baby’s developing eyes, especially the retina, which helps them see light and dark. For moms, getting enough can prevent night blindness, a condition where it is harder to see in low light, which sometimes happens during pregnancy if vitamin A levels are too low.
Supports Healthy Pregnancy Outcomes: Vitamin A plays a key role in pregnancy by reducing the risks of preterm birth. Research suggests adequate vitamin A status helps regulate placental function and supports optimal fetal development.
Mindsmaking
Risks of Vitamin A Deficiency in Pregnancy
While too much Vitamin A during pregnancy can be harmful, a deficiency is not an option. Vitamin A deficiency is one of the leading causes of blindness and can have serious consequences for both mother and baby. (6)
- Vitamin A deficiency can cause night blindness, making it difficult to see in low light or at night.
- It can lead to dry eyes, or xerophthalmia, which may result in corneal damage and blindness.
- A lack of Vitamin A can impair fetal development, increasing the risk of birth defects and slow growth.
- It can weaken the immune system, making the mother more likely to get infections.
- Vitamin A deficiency may contribute to maternal anemia due to its role in red blood cell production.
- It can raise the risk of preterm birth and lead to complications during labor.
Read This Next
No posts available
Best Foods Rich in Vitamin A During Pregnancy
Incorporating a variety of vitamin A-rich foods into your diet is essential for meeting your nutritional needs during pregnancy. This vital nutrient occurs naturally in many foods and is also added to fortified products like milk and cereal. (3)
To meet the recommended intake of vitamin A that is beneficial to your health and the fetal development of your little one, consider consuming foods such as:
- Fish, like herring and salmon
- Green leafy vegetables and others like carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, spinach, cooked greens, tomatoes, red sweet peppers, broccoli, and winter squash (which is also a good source of potassium)
- Fruits, which include cantaloupe, mangos, and apricots
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Fortified foods: breakfast cereals, like grains.
- Eggs. Rich in vitamins (A, D, B12).
Vitamin A from Animal-based sources (such as eggs, dairy, and liver) provides the Vitamin in the form of retinol, which the body can use immediately.
Plant-based sources (like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach) contain provitamin A carotenoids, such as beta-carotene, which the body must convert into retinol before it can be used.
Since the body processes these forms differently, a balanced diet that includes both sources can help meet one's vitamin A needs during pregnanc.
To best retain vitamin A content, avoid overcooking. Methods like steaming, microwaving, roasting at moderate temperatures, and quick stir-frying are recommended as they reduce cooking time and water exposure, which can lead to vitamin loss. (4)
Maintaining appropriate vitamin A levels during pregnancy is crucial for your health and fetal development. Focus on a balanced diet rich in beta-carotene sources and consult your healthcare provider before considering supplements. (7)
Mindsmaking

Frequently Asked Questions
Can you take vitamin A supplements while pregnant?
Vitamin A supplements are only required if you live in an area where the Vitamin is deficient or if you have a condition that makes it difficult for your body to absorb the nutrient through diet. However, it is generally recommended to obtain Vitamin A from dietary sources.
What happens if you don’t get enough vitamin A during pregnancy?
Research has shown that too low levels of Vitamin A during pregnancy can lead to impaired fetal development, night blindness, maternal anemia, and a higher risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Which foods should I avoid due to high vitamin A content?
Avoid liver and liver products such as pâté as they contain high levels of preformed vitamin A, which can be harmful in excess during pregnancy.
Is beta-carotene a safe source of vitamin A for pregnant women?
Yes, research shows that beta-carotene is a safe and essential source of vitamin A for pregnant women. Unlike preformed vitamin A (retinol) found in animal sources, beta-carotene is a provitamin A carotenoid that the body converts into vitamin A as needed. This reduces the risk of toxicity, which can be a concern with excessive intake of retinol during pregnancy.
How do I know if I’m getting too much vitamin A?
Too much Vitamin A can be very harmful, and symptoms such as Headaches, nausea and vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision, and skin changes such as dryness, itchiness, or yellowing often accompany it.
Was this article helpful?
How many stars are you giving this article?
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published.









































