Pregnancy Weight Gain Tracker
Input your current weight, and we'll guide you with weekly recommendations tailored to your state.
How to Calculate your pregnancy weight gain
Written by Mindsmaking Medical Writer
Fact Checked by Mindsmaking Professionals
24th February, 2025
Our Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator is a simple and reliable tool that is designed to help you track recommended weight gain throughout your pregnancy. It takes into account factors like your height, pre-pregnancy weight, and current weight, among others, to give you personalized results.
Healthy weight gain during pregnancy plays an important role in promoting both your well-being and your baby’s. Gaining the right amount of weight helps ensure your baby’s proper growth and development while also reducing the risk of complications [1].
Using our calculator will help you stay informed and confident in managing your pregnancy health, supporting the best outcomes for both you and your baby.
Key Takeaways
Track your pregnancy progress each week with our calculator—just enter your pre-pregnancy weight, current weight, height, and gestational age to monitor and stay within healthy weight gain ranges.
If you had a normal BMI (18.5–24.9) before pregnancy, the recommended weight gain for one baby is 11–16 kg, according to the Institute of Medicine.
Understand that your pregnancy weight gain is primarily from your baby's growth and bodily changes, not just fat.
Excess pregnancy weight gain increases risks like diabetes, C-section, and obesity for both mother and baby.
Healthy pregnancy weight gain depends on your pre-pregnancy BMI. Balanced eating and regular weight checks support your baby’s growth and help prevent pregnancy complications.
How Our Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator Works
Our Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator is designed to give you a personalized, medically-informed guide to healthy weight gain throughout your pregnancy. By entering just a few key details—your pre-pregnancy weight, current weight, height, and gestational age (how many weeks pregnant you are)—you’ll receive a tailored recommendation based on guidelines from the Institute of Medicine (IOM) [2] [18] .
Using this information, the calculator determines your pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI) and classifies it as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. Based on your BMI, our advanced system calculates a personalized weight gain range for your current week of pregnancy, and also provides guidance for the weeks ahead, helping you track your progress and stay within a healthy range throughout your pregnancy journey.
This assessment is vital in supporting the well-being of both you and your baby. Maintaining a healthy weight gain can reduce the risk of complications related to gaining too little or too much weight. While our calculator provides valuable insight, it’s designed to complement, not replace, advice from your healthcare provider. Always consult with your midwife, doctor, or health professional for personalized care.
For the Best Experience: Use the App
To get the most out of your weight gain tracking, we recommend using our free app, which allows you to update your details weekly for more accurate, real-time guidance. Our app includes features like:
- Trimester-based weight gain tracking
- Progress charts
- Weekly reminders
- Tips tailored to your pregnancy stage
Download the Mindsmaking Baby App now to enjoy a more personalized and supportive experience on your journey to a healthy pregnancy.
How Much Weight Should I Gain During Pregnancy?
The amount of weight you should gain during pregnancy largely depends on several factors. Your pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI), whether you are carrying one or more than one baby, and your overall health status all play a role in determining the right amount of weight you should gain.
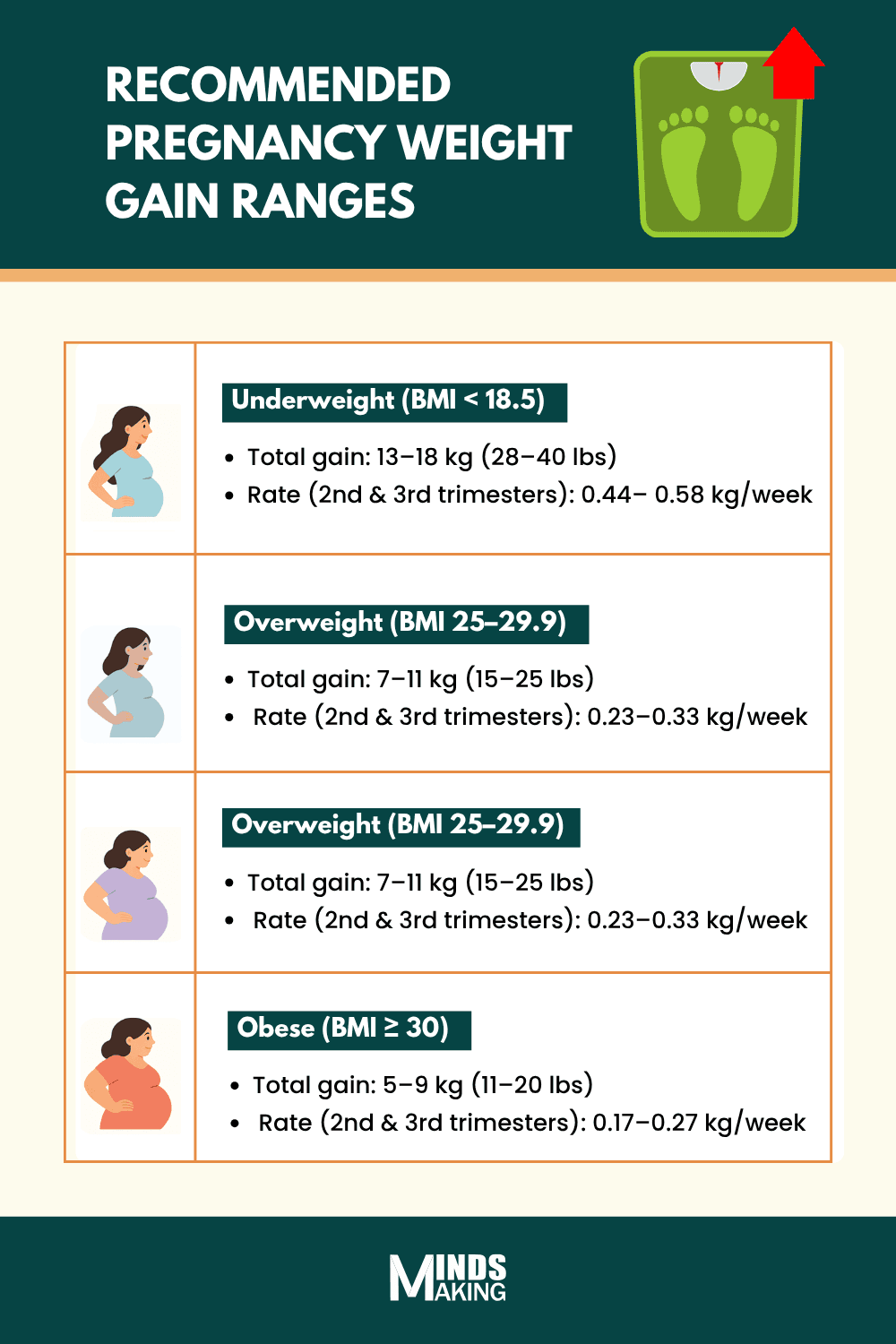
According to the Institute of Medicine (IOM), there are standard ranges for healthy weight gain during pregnancy. If you are carrying a single baby, here are the recommended ranges [3] [19].
- Underweight (BMI less than 18.5): 13-18 kg (28–40 lbs)
- Normal weight (BMI between 18.5 to 24.9): 11-16 kg (25–35 lbs)
- Overweight (BMI between 25 to 29.9): 7-11 kg (15–25 lbs)
- Obese (BMI greater than 30): 5-9 kg (11–20 lbs)
Weight gain during pregnancy isn’t evenly spread out across all trimesters. There are standard guidelines that vary by trimester, with weight gain typically increasing during the second and third trimesters. In fact, the average rate of gain in the second trimester may be slightly higher than in the third [17]. Based on your pre-pregnancy BMI, the recommended weekly weight gain during these trimesters is as follows[19]:
- Underweight (BMI less than 18.5): 0.45–0.59 kg/week (1.0–1.3 lbs)
- Normal weight (BMI between 18.5 to 24.9): 0.36–0.45 kg/week (0.8–1.0 lbs)
- Overweight (BMI between 25 to 29.9): 0.23–0.32 kg/week (0.5–0.7 lbs)
- Obese (BMI greater than 30): 0.18–0.27 kg/week (0.4–0.6 lbs)
How Much Weight Should You Gain with Twins?
If you are carrying twins, greater weight gain is expected [3]. However, the IOM guidelines acknowledge that there is not enough data to establish specific weight gain recommendations for women carrying triplets or higher-order multiples. The standard range of weight gain for twin pregnancies is as follows [2] [19]:
- Normal weight (BMI between 18.5 to 24.9): 16.8–24.5 kg (37-54 lbs)
- Overweight (BMI between 25 to 29.9): 14.1–22.7 kg (31-50 lbs)
- Obese (BMI greater than 30): 11.3–19.1 kg (25-42 lbs)
Proper weight gain is important because it supports your baby's development and reduces the risk of complications, as excessive gestational weight gain has been associated with adverse outcomes such as preterm birth, gestational diabetes, and pre-eclampsia. It also supports your own health by minimizing postpartum weight retention and delivery complications [5].
However, it is important to note that every pregnancy is different. While these guidelines are helpful, your doctor can give you the most accurate recommendations specific to your health needs as your pregnancy progresses. Always consult your healthcare provider to monitor your progress and adjust your weight gain goals as needed.
Mindsmaking
What Contributes to Weight Gain In Pregnancy?
About 35% of your total pregnancy weight gain comes from the baby, placenta, and amniotic fluid — all essential for your baby’s growth and protection. The rest of the weight comes from your body preparing for pregnancy and birth, including increased blood volume, a growing uterus, larger breasts, extra fluids, and fat stores to support labor, delivery, and breastfeeding [4].
Uterus
Your uterus undergoes remarkable changes during pregnancy to support your developing baby. Starting from a non-pregnant weight of about 70 grams, it expands significantly by full term, transforming into a thin-walled, muscular organ designed to hold the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid [16]. By the end of pregnancy, the uterus can weigh between 1 and 2.5 kilograms [15]. This dramatic growth is a major contributor to the overall weight gain you experience during pregnancy.
Maternal Blood Volume
One important factor is the increase in your blood volume. During pregnancy, your blood volume expands and makes up about 10% of the total weight you gain. Your plasma—the liquid part of your blood—increases by around 50%, while red blood cell mass also grows steadily to support your baby’s needs. Most of this plasma growth happens by week 34, and iron supplements can help your body keep up with this increase. This extra blood helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to your growing baby, so it’s a key part of healthy pregnancy weight gain [17].
Total Body Water
During pregnancy, your body holds about 7 to 8 extra liters of water. Most of this—around 6 to 7 liters—helps support your baby by building up the fluid around your cells. This extra water is shared between your baby, the placenta, amniotic fluid, your uterus, breasts, blood, and other tissues.
Your hormones are working hard behind the scenes to help your body hold onto this fluid and keep everything in balance as your pregnancy progresses.[6]. While it may not always feel noticeable, this water weight is a normal and essential part of a healthy pregnancy.
Placenta
The placenta is a key contributor to pregnancy weight gain, both in physical weight and how it affects your body’s metabolism. It weighs about 500 grams and produces hormones that influence how your body stores and uses energy. In early pregnancy, these hormones boost appetite and encourage fat storage.
Later on, they help release that stored energy to support your baby’s growth and prepare you for breastfeeding. So, the placenta not only adds to your weight directly but also plays a major role in managing how your body gains and uses weight during pregnancy[10].
Protein
Protein buildup is another key factor that contributes to weight gain during pregnancy. During pregnancy, your body stores about 686 grams of protein, with the largest portion—around 42%—going to your growing baby [6]. Smaller amounts support the uterus, blood, placenta, and breasts. This protein buildup increases gradually but peaks in the third trimester, when most fetal growth and maternal tissue expansion occur. These estimates come from studies using total body potassium, a method used to measure changes in body protein [13].
Fetus
By the time you reach full term, your baby will weigh around 3.2 to 3.6 kilograms [9]—about a third of the total weight you gain during pregnancy. Most of this growth happens in the third trimester when your baby rapidly builds fat and protein, growing more than four times between weeks 26 and 40. By the end of pregnancy, fat makes up roughly 14% of your baby’s birth weight, with daily fat gains of 1.6 to 3.4 grams per kilogram [14].
But it’s not just your baby getting bigger—your body is also storing extra fat and protein to fuel this growth and prepare you for breastfeeding. That’s why your weight gain during pregnancy is so important and totally natural [13].
Mindsmaking

When Is Pregnancy Weight Gain Too Much?
Pregnancy weight gain is considered too much when it goes beyond the recommended range for your pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI). For example, if you had a normal BMI (18.5–24.9) before pregnancy, the Institute of Medicine (IOM) recommends gaining between 11 and 16 kg (25–35 lbs). If you gain significantly more than that, it may be considered excessive.
Health Risks for the Mother
Excess maternal weight gain is a significant cause of various health complications, such as metabolic complications, high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, and a greater likelihood of needing a cesarean section. Mothers may also struggle with retaining weight after birth [1]. This postpartum weight retention can contribute to long-term obesity, increasing the risk for a range of chronic diseases in the future.
Health Risks for the Baby
Excessive gestational weight gain (GWG) can have significant consequences for the baby’s health. One of these consequences is macrosomia [1], high birth weight typically over 4,000–4,500 grams (8 lbs 13 oz to 9 lbs 15 oz.). Babies born with macrosomia face increased morbidity and mortality risks, including stillbirth and long-term complications like brachial plexus injury [7].
Long-term Impact
In the long term, children born to mothers who gained more than the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy are more likely to develop childhood obesity and related metabolic disorders [7]. These children are at higher risk for insulin resistance and may carry excess weight into adolescence and adulthood, contributing to chronic health issues later in life.
Mindsmaking

How to Maintain Healthy Weight Gain and Balanced Nutrition During Pregnancy
Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy is about balance, not eating for two, but eating smart for two. Regularly tracking your pregnancy weight helps your healthcare provider give personalized nutritional and lifestyle advice. A well-balanced, nutrient-rich pregnancy diet supports your baby’s development while helping you avoid excessive weight gain that could lead to complications.
Your pre-pregnancy nutrition and dietary habits during pregnancy play a key role in your baby’s health [8]. Studies show that women who follow health-conscious eating patterns—including whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables—are less likely to experience pregnancy complications and may have better child health outcomes [8].
Being mindful of portion sizes, limiting processed foods, and incorporating safe pregnancy exercise can also help you stay within the recommended weight range while supporting both your energy levels and your baby’s growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a pregnancy weight gain calculator?
A pregnancy weight gain calculator is a simple tool that uses information like your height, pre-pregnancy weight, current weight, and gestational age to provide personalized guidance on how much weight you should ideally gain to support your health and your baby's development.
Is it normal to gain more or less than the recommended amount?
Yes, it is normal for weight gain to vary from the recommended range because every pregnancy is different. However, gaining significantly more or less than the recommended amount can increase health risks for both mother and baby.
How accurate are pregnancy weight gain calculators?
Pregnancy weight gain calculators provide accurate recommendations based on your pre-pregnancy BMI and other key factors. They help to track your progress, but they should not replace advice from your doctor, who can consider your overall health and pregnancy specifics.
What if I'm pregnant with twins?
If you’re pregnant with twins, the recommended weight gain is higher than for a single baby. For example, normal weight women carrying twins should aim to gain about 16.8 to 24.5 kg.
Can I lose weight during pregnancy if I’m overweight?
Generally, losing weight during pregnancy is not recommended. However, personalized care and clinical judgment are necessary in the management of the overweight or obese woman who is gaining (or wishes to gain) less weight than recommended.
Do all pregnant women need to track their weight?
It is recommended that all women actively track weight, as monitoring weight gain is important for maternal and fetal health. Tracking helps ensure you stay within a healthy range and allows your healthcare provider to give appropriate nutritional and lifestyle guidance.
Can the calculator tell me if I’m gaining too much or too little?
Yes, our pregnancy weight gain calculator can indicate if your weight gain is within the recommended range or if you are gaining too much or too little, based on your pre-pregnancy BMI and gestational age. Updating your information improves the accuracy of this feedback.
Is weight gain different for each trimester?
Yes, weight gain is not evenly distributed throughout pregnancy. Studies suggest an average gain of approximately 0.45 kg (1 lb) per week during the second trimester and a slightly lower gain of about 0.40 kg (0.9 lb) per week during the third trimester.
Should I be concerned if my weight gain fluctuates?
Some natural fluctuations in weight during pregnancy are normal due to changes in fluid retention, food intake, and fetal growth patterns. However, if you notice sudden or significant fluctuations, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider.