Pregnancy Gingivitis
Getty Image Signature
Written by Mindsmaking Medical Writer
Fact Checked by Mindsmaking Professionals
4th, June, 2025
Bleeding gums in pregnancy are common, but not harmless. Learn what causes them, how to treat and prevent pregnancy gingivitis, and the best diet tips to keep your smile healthy throughout pregnancy.
During pregnancy, if you notice your gums feeling extra sensitive, puffy, or bleeding a little when you brush, do not be scared; you are not alone. Research shows that 60 to 75% of pregnant women experience some form of gum inflammation. This common condition is known as pregnancy gingivitis, and it is mostly due to the natural hormonal changes your body is going through. (5)
Though it may seem like a minor problem, it is important to address it. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more serious pregnancy complications and dental issues later on. But with gentle brushing, regular dental checkups, and good oral hygiene, your gums can be kept clean and healthy throughout your pregnancy.
Key Takeaways
Research shows that 60 to 75% of pregnant women experience some form of gum inflammation.
Pregnancy gingivitis can occur anytime between the second and eighth month, but can worsen, especially during the second trimester.
During pregnancy, a rise in hormones like estrogen and progesterone makes your gums extra sensitive, so even a small amount of plaque can cause swelling, redness, and bleeding.
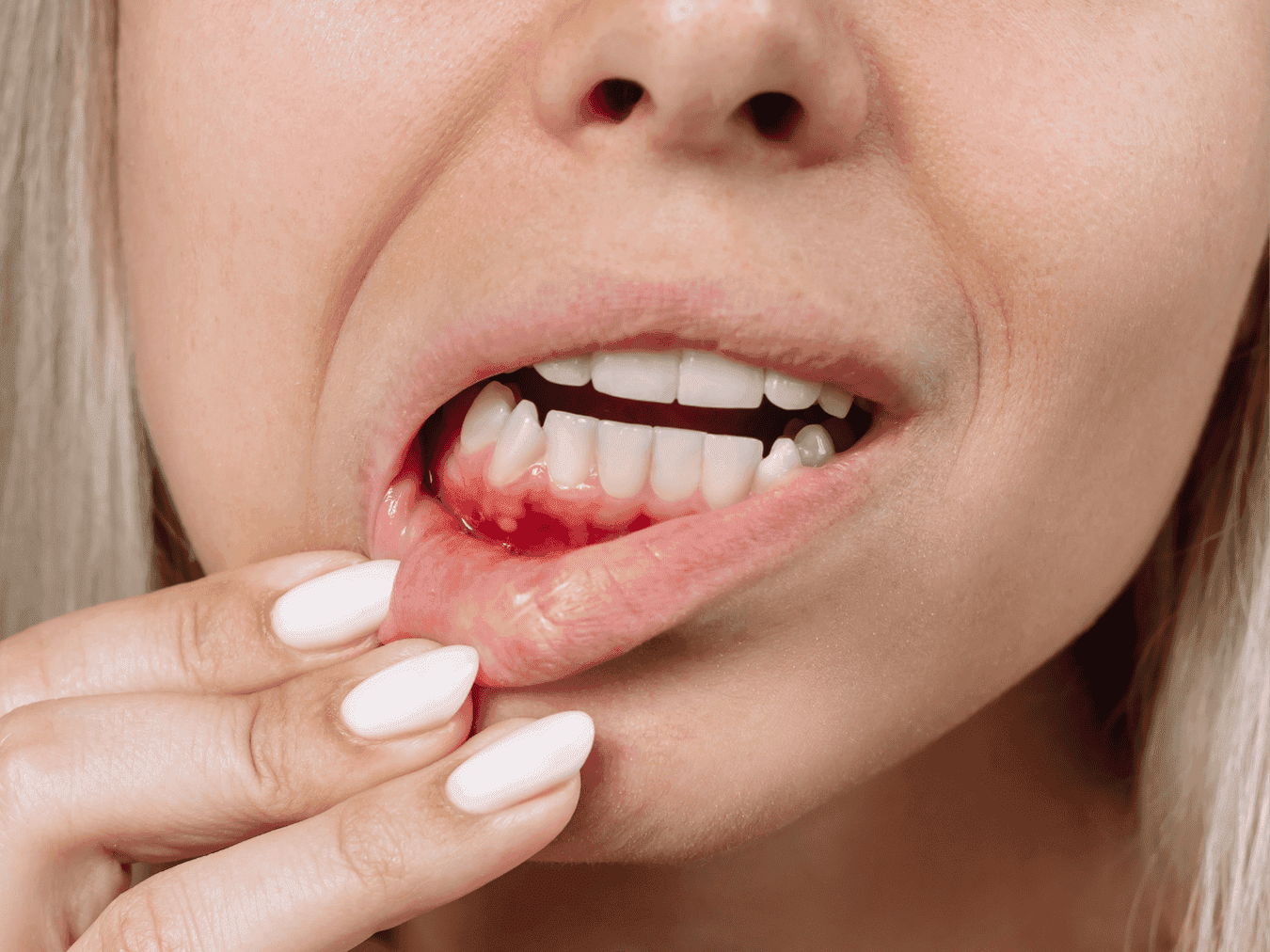
The symptoms of pregnancy gingivitis can be easily identified. They often include swelling or “puffy” gums, tender gums, bleeding gums when brushing or flossing, redness in the gum tissue, and loose teeth.
Brushing and flossing daily, eating vitamin-rich foods, rinsing with salt water, and keeping up with safe dental checkups can help keep your gums healthy.
To prevent pregnancy gingivitis, focus on good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and a healthy diet. Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and drink alcohol-free mouthwash.
What Is Pregnancy Gingivitis?
Pregnancy gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, also known as swollen gums. Swollen gums during pregnancy may be sore and more prone to bleeding. It is caused by hormonal changes that increase the blood flow to the gum tissue and cause the gums to be more sensitive, irritable, and swollen. (1)
Pregnancy gingivitis makes your gums overreact to even small amounts of plaque. Regular gingivitis, also called plaque-induced gingivitis, is mainly caused by poor oral hygiene. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, and if not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. Other factors like crowded or misaligned teeth, poorly fitted dental prosthetics, or hard-to-reach areas can make plaque removal difficult, increasing the risk of gingivitis. (10)
Pregnancy gingivitis can develop at any point between the second and eighth month of pregnancy, with symptoms often peaking during the second trimester. In most cases, it improves or resolves after childbirth with proper oral care (1) (7).
What Causes Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy?
One of the main reasons for bleeding gums during pregnancy is hormonal changes, especially the rise in progesterone and estrogen. The rising levels of estrogen and progesterone support your growing baby and make the gums more sensitive to plaque. These hormones increase blood flow and cause the blood vessels to dilate more easily, leading to a stronger inflammatory response in the gum tissues (12).
So, a small amount of plaque can trigger redness, swelling, and bleeding. Gum cells have receptors that respond to estrogen, especially in areas like the outer layers of the gums and the connective tissue beneath. When these hormones rise during pregnancy, the gums react more to bacteria along the gumline. (10)
In addition to hormonal changes, certain physical changes during pregnancy, such as morning sickness (which exposes the teeth and gums to stomach acid), more frequent snacking or cravings for sugary foods, and reduced saliva production, can also worsen pregnancy gingivitis. These factors contribute to plaque buildup and weaken tooth enamel, which can further irritate the gums (4).
Teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism) can place extra pressure on the gums, potentially leading to bleeding. Smoking and the use of tobacco products can also compromise oral health, increasing the risk of gum issues. In pregnancy, these habits pose additional health risks to both the mother and the unborn baby. (13)
Signs and Symptoms of Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy
Pregnancy gingivitis symptoms may include swollen or “puffy” gums, tenderness, bleeding during brushing or flossing, redness in the gum tissue, and even loose teeth. (14)
Other signs and symptoms include: (11)
- Red, swollen, or tender gum tissue
- Receding gums
- Sensitive teeth
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
- Teeth that become loose or wobbly
- Bad breath
Bleeding gums during pregnancy are common and usually not a cause for concern. Hormonal changes can make gums more sensitive, making them more likely to bleed when brushing or flossing. But if your gums are bleeding frequently, feel swollen, or look dark red, it could be a sign of untreated gum disease.
Risk of Pregnancy Gingivitis
If left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. This condition causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating deep pockets that harbor bacteria. Over time, it can lead to gum recession, bone damage, and even tooth loss(9).
For pregnant women, the concerns are not just dental. Research has shown a potential link between advanced gum disease and complications like preterm birth and low birth weight. While more studies are needed to confirm the extent of this connection, addressing gum disease early in pregnancy is essential for both your oral health and your baby’s well-being (8).
Read This Next
No posts available
How can I Treat Bleeding Gums In Pregnancy?
Bleeding gums during pregnancy are often a sign of pregnancy gingivitis, caused by hormonal changes or poor oral hygiene. Dr. Joyce Kahng, a Korean-American cosmetic dentist, recommends improving your brushing and flossing routine and using a water flosser to help reduce symptoms. If hormones are the cause, symptoms usually improve during or after pregnancy. Keep up your oral hygiene and always inform your dentist before starting any dental treatment.
Make it a habit to brush twice daily and floss at least once a day to keep your mouth healthy. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush can help if your gums feel sensitive. Do not skip your regular dental checkups, and let your dentist know if anything feels off. (1)
Natural Remedies for Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy
Bleeding gums during pregnancy can be managed with simple home remedies and a focus on good oral hygiene.
Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your teeth gently but thoroughly twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Do not rush; spend at least two minutes brushing. Floss at least once daily to remove plaque buildup between teeth and prevent gum irritation (17).
Load up on Vitamin C: Vitamin C strengthens the immune system and helps the gums fight off bacteria that cause bleeding and inflammation. You can get it from citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, or you can take a supplement if recommended by your doctor.
Be Mindful of Vitamin A: Vitamin A supports gum and tooth health, but be careful not to overdo it. Too much can be harmful during pregnancy, so stick to the recommended daily intake. Sweet potatoes, carrots, and leafy greens are great natural sources.
Try a Salt Water Rinse: Gargling warm salt water can soothe inflamed gums and reduce bacteria. Mix about half a teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish gently, do not swallow.
Rinse After Morning Sickness: Vomiting exposes the teeth and gums to stomach acid, which can erode enamel and irritate gum tissue, making gingivitis worse. Do not brush immediately afterward. Instead, rinse your mouth with water or a mouthwash to protect your enamel from stomach acids. (11)
When Should I See My Doctor for Bleeding Gums?
You should talk to your dentist if you notice any unusual bumps on your gums during pregnancy. These could be pregnancy tumors, harmless growths caused by hormonal changes that usually disappear after birth. Still, it’s best to have them checked to rule out anything serious.
Routine dental cleanings and exams are safe throughout pregnancy and are one of the most effective ways to manage bleeding gums. These cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup, which helps reduce inflammation and stops the bleeding.
If your dentist notices more advanced gum disease signs, they may recommend a deeper cleaning called scaling and root planing. This procedure cleans below the gumline to remove bacteria and smooth the roots of your teeth, helping gums heal and reattach properly. Local anesthetics like lidocaine, commonly used during these treatments, are considered safe for pregnant women, especially when used in recommended doses.
Your dentist may also prescribe a pregnancy-safe antimicrobial rinse, such as chlorhexidine, to help reduce bacteria and control gum inflammation. To ensure safety during pregnancy, it is best to use only those specifically recommended by your healthcare provider.
Dental X-rays are generally safe when necessary, as modern equipment uses very low doses of radiation and includes protective shielding. But they should be limited to urgent situations during pregnancy. Always let your dentist know you're pregnant so they can tailor your treatment plan and medication choices accordingly. (3), (4)
Mindsmaking
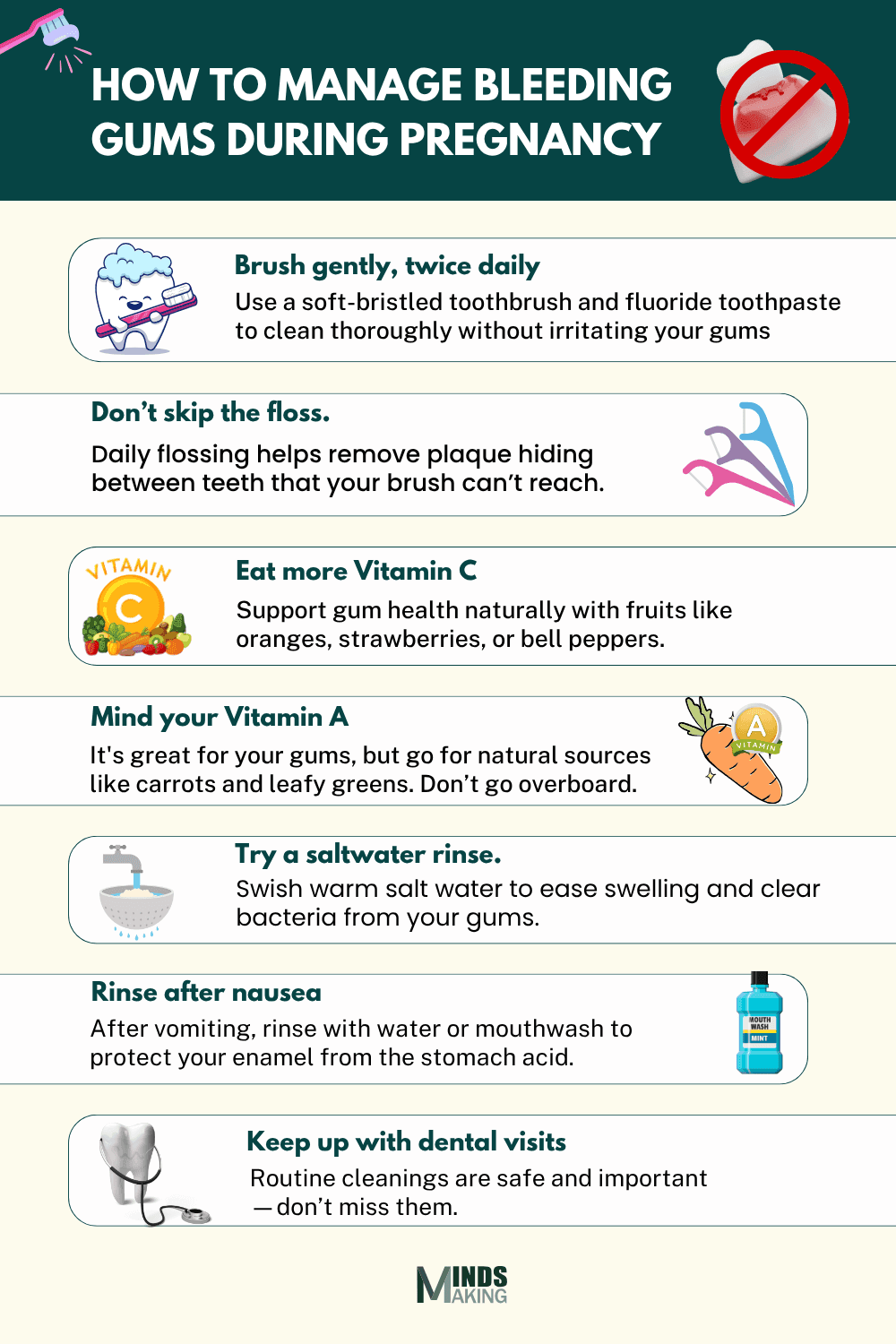
Tips to Prevent Bleeding Gums in Pregnancy
Dr. Joyce Kahng, a dentist, explains that prenatal dental care is important for both your oral health and your baby’s health. She recommends seeing your dentist regularly, especially if you’re trying to conceive or in your first trimester. This allows you to identify and plan any necessary treatments early. That way, during your second trimester—when you’re typically more comfortable and morning sickness has eased—you can safely complete any dental work that might otherwise turn into an emergency later in pregnancy.
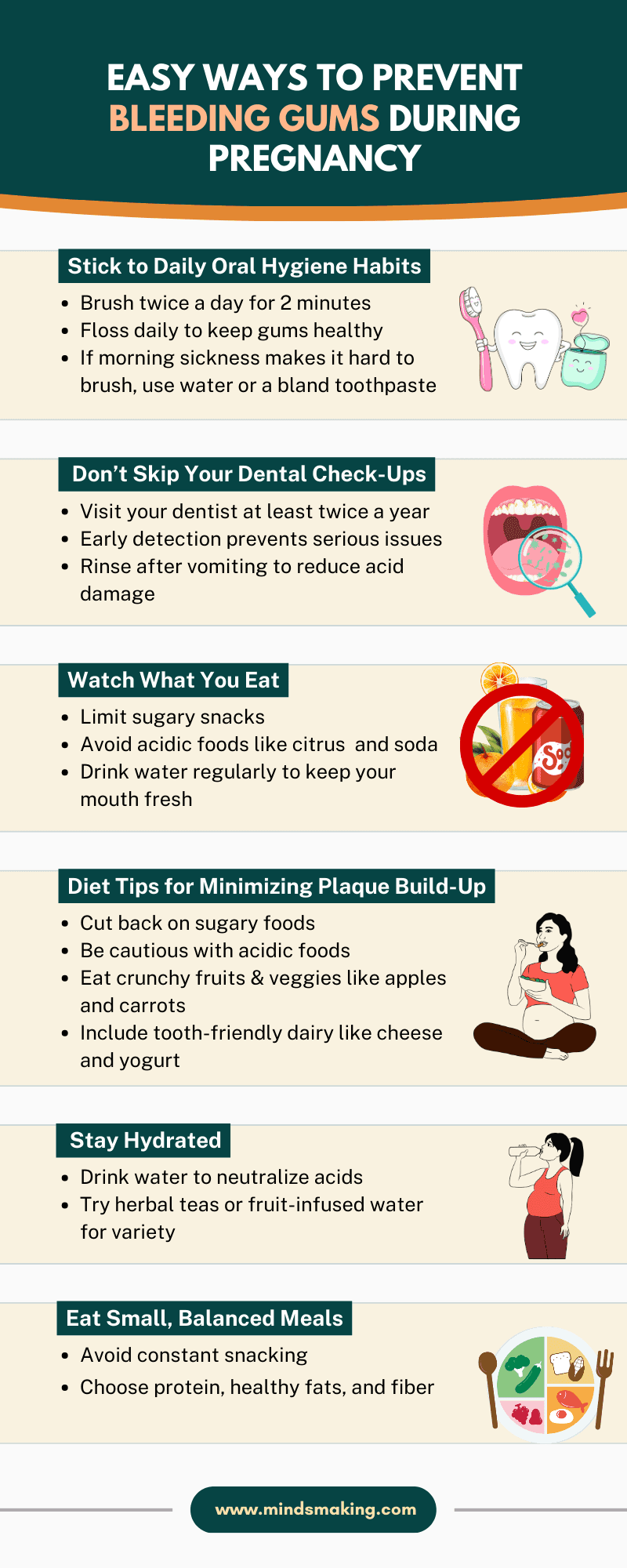
Stick to Daily Oral Hygiene Habits: Brush twice daily for two minutes and floss daily because they are your best defenses against bleeding gums during pregnancy. Hormonal changes make your gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation, so skipping your routine even for a few days can lead to gingivitis. If morning sickness makes brushing tough, use just water or switch to a bland toothpaste and rinse with a fluoride mouthwash. It is easier to maintain the habit than to restart it once your gums are irritated.
Don’t Skip Your Dental Check-Ups: Even if your schedule is packed with prenatal appointments, don’t neglect the dentist. Visit at least twice yearly because it helps to catch gum issues early before they become painful or more serious. Your dental team can spot trouble areas and do deep cleanings if needed.
Watch What You Eat: A tooth-friendly pregnancy diet helps prevent plaque build-up and gum irritation. Avoid sugary snacks that feed bacteria and acidic foods like citrus or sodas that wear down enamel. Drinking water regularly and maintaining your oral care routine will go a long way in keeping your gums healthy, even if cravings hit. (14)
Diet Tips for Minimising Plaque Build-up
Your diet plays a huge role in the health of your gums, especially during pregnancy when hormonal changes can intensify inflammation and increase plaque accumulation. Making smart food choices can help protect your teeth and gums from damage. (6)
Cut Back on Sugar: When you eat sugary snacks or drinks, bacteria in your mouth feed on that sugar and release acid as a byproduct. This acid attacks the enamel and irritates your gums. Avoid sticky candies, sugary beverages (like soda or sweetened teas), and processed carbs like white bread and pastries, which quickly turn into sugar in your mouth.
Watch Out for Acidic Foods: Some foods are naturally acidic, harming your enamel and aggravating gum tissue. These foods include citrus fruits (like oranges and lemons), tomatoes, vinegar-based dressings, and carbonated drinks. You don’t have to eliminate them, but eat them in moderation and rinse your mouth with water afterwards to neutralize the acid.
Eat More Tooth-Friendly Foods: Crunchy, fibrous fruits and vegetables like apples, carrots, and celery help naturally clean your teeth as you chew and stimulate saliva flow, which helps wash away food particles and bacteria. Dairy products like cheese, yogurt, and milk are rich in calcium and phosphorus, which help strengthen enamel and support bone health, including the bone that supports your teeth.
Stay Hydrated: Water is your secret weapon. It keeps your mouth moist, helps neutralize acids, and flushes away food particles and bacteria. Drinking water after meals and snacks can help reduce plaque buildup between brushes. Opt for unsweetened herbal teas or fruit-infused water if you're craving something flavored.
Eat Small, Balanced Meals: Frequent snacking, especially on sugary or carb-heavy foods, keeps your mouth in a constant acid-producing state. Try to eat balanced meals with protein, healthy fats, and fiber to stay full longer and reduce the need for between-meal snacks. If you snack, choose healthy foods, like fruits or vegetables, and rinse your mouth afterward. (6)
Mindsmaking
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it normal for gums to bleed during pregnancy?
Yes, bleeding gums during pregnancy are quite common and generally not a cause for major concern. It's often referred to as pregnancy gingivitis and is due to hormonal changes that make gums more sensitive to plaque and inflammation.
When does pregnancy gingivitis typically start?
Pregnancy gingivitis can occur anytime between the second and eighth month but can worsen, especially during the second trimester, and will disappear once your baby is born.
Can pregnancy gingivitis harm my baby?
Pregnancy gingivitis itself is unlikely to directly harm the baby, but if left untreated, it can lead to periodontitis, which has been linked to an increased risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. However, mild red or swollen gums are not typically harmful to the fetus.
Can I get a dental cleaning while pregnant?
Yes, getting dental cleaning while pregnant is safe and recommended. It's important to maintain good oral hygiene throughout pregnancy for the health of both the mother and the baby.
Can pregnancy gingivitis go away after delivery?
Yes, pregnancy gingivitis, a common condition during pregnancy, typically resolves after delivery when hormonal changes return to normal. The increased blood supply to the gums during pregnancy, which makes them more sensitive to bacteria, after pregnancy, this extra blood flow diminishes, and the gingivitis usually subsides.
Should I use mouthwash if I have bleeding gums during pregnancy?
Yes, it is generally safe and even recommended to use mouthwash during pregnancy, especially if you're experiencing bleeding gums. However, choose an alcohol-free, fluoridated mouthwash.
How often should I visit the dentist while pregnant?
It is generally recommended to visit the dentist at least once during your pregnancy, ideally in your second trimester. Let your dentist know you're pregnant. This is important to maintain oral health and address potential pregnancy-related dental issues.
How can diet help with pregnancy gingivitis?
A diet rich in certain nutrients can help support gum health and potentially reduce the severity of pregnancy gingivitis. Focus on nutrient-rich foods from all the food groups, like fruits, vegetables, protein foods, calcium-rich foods, and whole grains.
Can stress during pregnancy worsen gum problems?
Yes, stress during pregnancy can worsen gum problems, specifically gingivitis and other forms of gum disease. Stress hormones, like cortisol, can increase inflammation and weaken the immune system, making gums more susceptible to infection and bleeding.
Can swollen gums make eating painful during pregnancy?
Yes, swollen gums can make eating painful during pregnancy. Swollen, red, and tender gums, a common symptom of pregnancy gingivitis, can make chewing and eating uncomfortable or even painful.
How can I prevent pregnancy gingivitis?
To prevent pregnancy gingivitis, focus on good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and a healthy diet. Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and drink alcohol-free mouthwash. Limit sugary foods and drinks, and seek professional dental care throughout pregnancy.
Can pregnancy gingivitis go away on its own?
Yes, pregnancy gingivitis often resolves on its own after delivery, as it is linked to hormonal changes in pregnancy.
Can pregnancy gingivitis lead to other health problems?
Yes, pregnancy gingivitis, if left untreated, can lead to more serious health problems for both the mother and the baby. It can progress to periodontitis, which has been linked to preterm birth, low birth weight, and other pregnancy complications.
Was this article helpful?
How many stars are you giving this article?
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published.









































